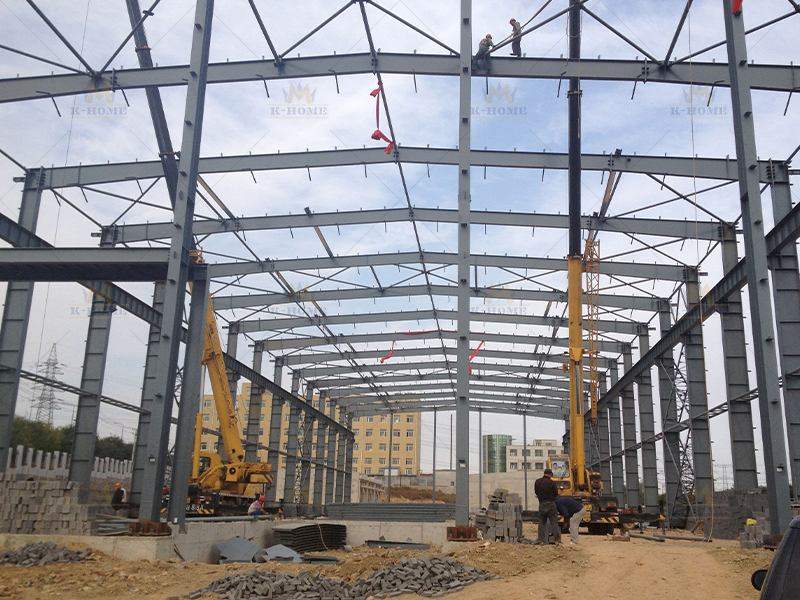
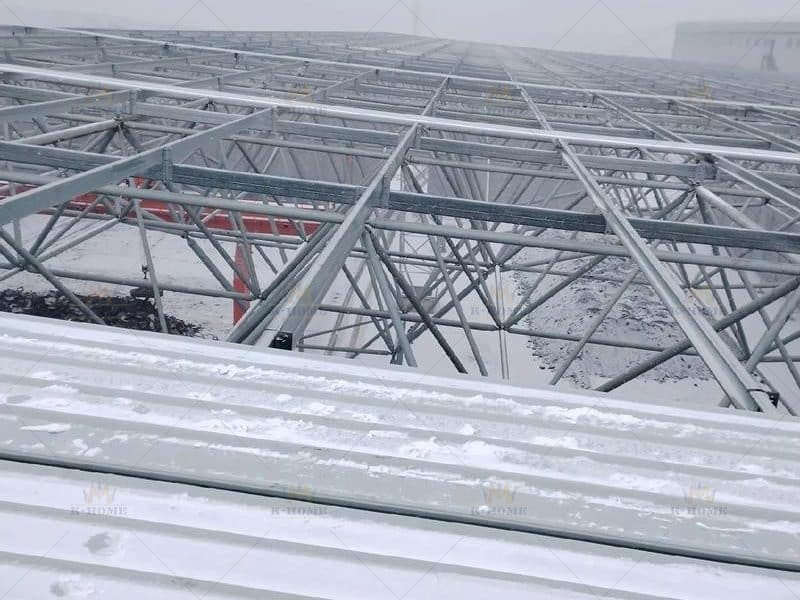
In simple terms, Steel Frame Structure Installation refers to taking pre-fabricated steel components—like steel columns, steel beams, and steel trusses—that are produced in advance by the factory, then assembling, joining, and securing them step by step on the construction site according to the requirements of the architectural design drawings, and finally building the load-bearing frame of the building.
It has a very close connection with “steel structure installation“; the former is the most core step of the latter. Meanwhile, “frame structure steel” is relied on throughout the entire steel frame installation process, and the load-bearing capacity and stability of the structural steel frame are directly related to it.
Steel Frame Structure Installation: How to Complete Preliminary Foundation Preparation Well?
Preliminary preparation is the basis for the smooth progress of steel frame structure installation. Overlooking preliminary preparation details can easily lead to rework later, affecting overall efficiency. Carefully analyzing the key points of initial preparation for steel structure installation helps avoid potential risks.
Clarify Technical Standards and Requirements for Steel Frame Installation
Before starting the steel frame installation, technical personnel need to be familiar with construction drawings, check the dimensions, joint structures, and material specifications of the steel frame, and clarify the design intent. If necessary, conduct a detailed design, and the detailed drawings must be reviewed and approved by the original design unit. Develop a special construction plan, specifying the operation methods, quality standards, and resource allocation for each process. After approval, conduct technical disclosure to construction personnel. At the same time, determine the measurement and setting-out plan, and clarify the layout of the control network and the positioning accuracy of components.
Plan Operation Space to Improve On-Site Efficiency of Structural Steel Frame Construction
First, level and clean the site, dividing it into component storage, assembly, hoisting, and office zones—each with clear functions to avoid chaos. Harden heavy-vehicle routes and stacking areas as needed to ensure the foundation supports equipment and components, preventing settlement.
Next, set up temporary offices and material warehouses with water, electricity, and fire safety gear. Renovate access roads and hoisting zones to allow smooth transport and stable parking for vehicles and equipment.
Finally, using owner-provided reference points, establish on-site plane and elevation control networks with sturdy measurement points—laying a precise base for subsequent steel frame structure installation
Prepare Sufficient Materials and Personnel for Smooth Steel Frame Structure Installation
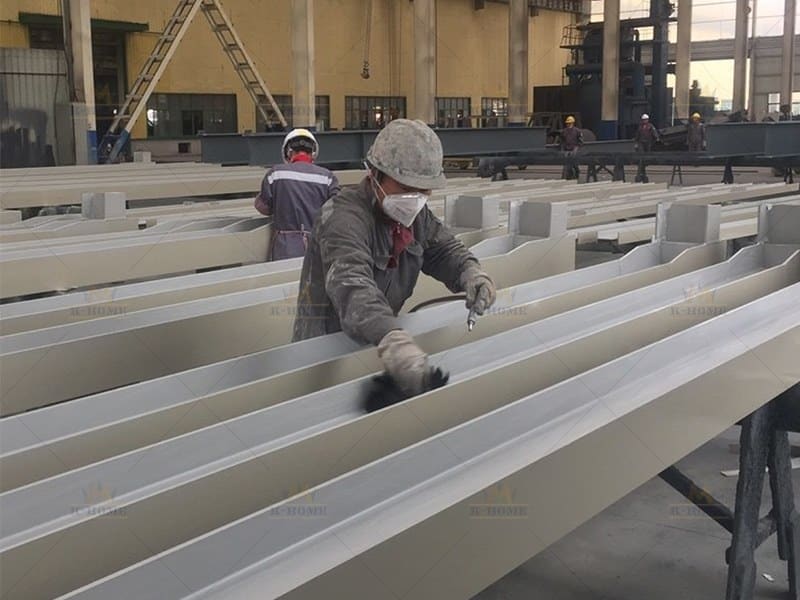
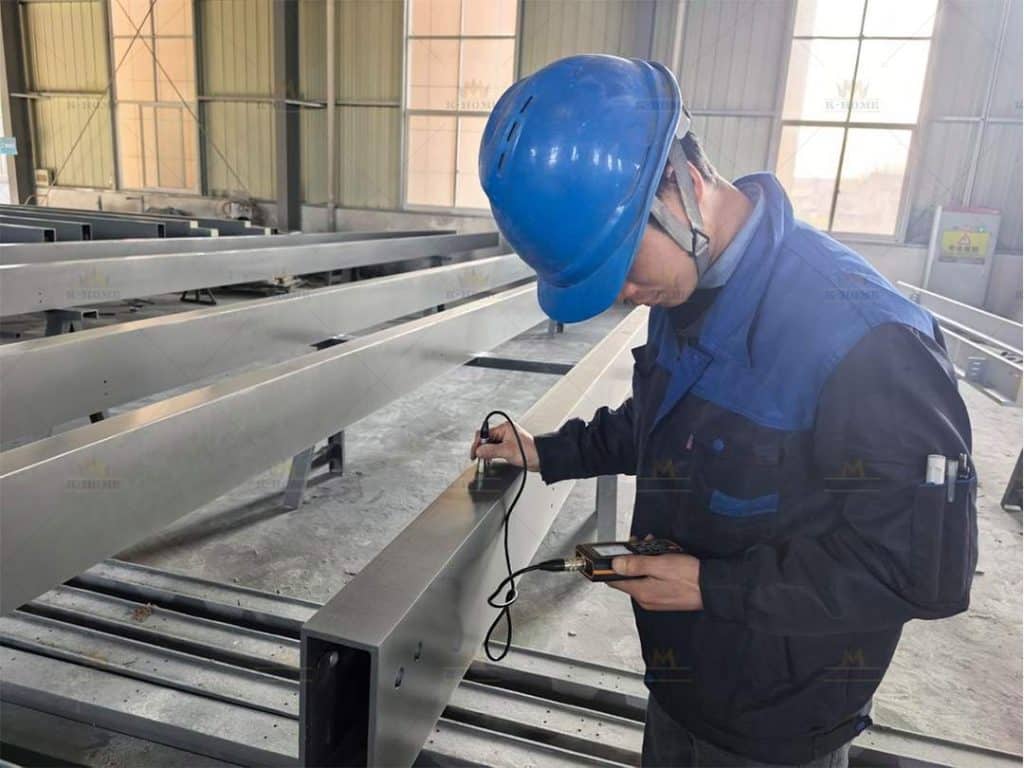
When steel structure components arrive at the site, check their specifications, models, and quantities, verify the qualification certificates and material certificates, and conduct random inspections on their appearance. Components with deformation or corrosion shall be returned directly. Connecting materials (high-strength bolts, welding rods) must meet design specs, with valid certificates and retest reports. Batch-test high-strength bolts for torque coefficient. Choose truck/crawler cranes and rigging based on component weight and height; prepare tools like theodolites and torque wrenches, ensuring measuring instruments are verified and valid. Assemble a professional team with clear roles. Ensure certified specialists (e.g., crane operators, welders) complete safety and technical training for steel framework.
Complete Implementation Process of Steel Frame Structure Installation
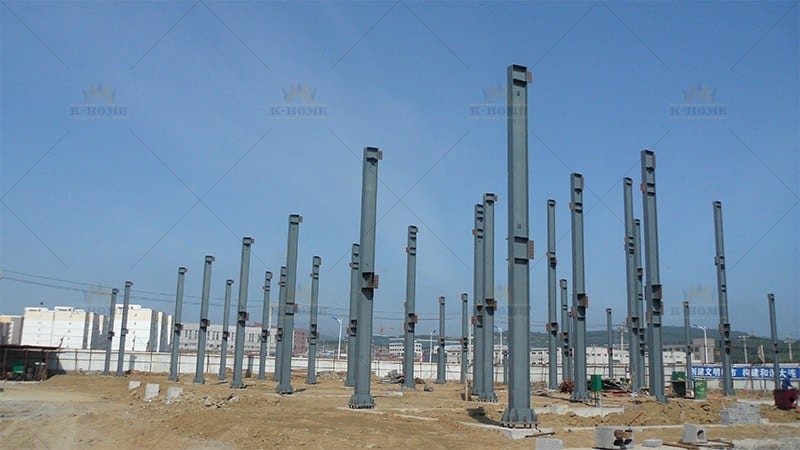
Step 1 for Steel Frame Erection: Prioritize Steel Structure Foundation Prep
The foundation is the basis for steel frame erection. First, determine the foundation type according to the building’s purpose (such as factory, office building) — for example, select pile foundations for factory load-bearing needs and independent foundations for office building stability, ensuring it matches the frame’s stress requirements. Three key tasks must be done well:
First, after the foundation construction is completed, it is necessary to verify whether its bearing capacity meets the design requirements to avoid settlement problems after subsequent frame installation; Second, measure the foundation surface elevation to ensure the error is controlled within the allowable range of specifications; Third, check the embedded bolts — as the core components connecting steel members to the foundation, it is necessary to inspect whether their position, verticality and exposed length meet the standards. Excessive position deviation will directly affect the installation accuracy of steel columns.
Step 2 of Steel Frame Installation: Inspection and Pretreatment of Prefabricated Steel Components
The foundation is the basis for steel frame erection. First, determine the foundation type according to the building’s purpose (such as factory, office building) — for example, select pile foundations for factory load-bearing needs and independent foundations for office building stability, ensuring it matches the frame’s stress requirements. Three key tasks must be done well:
- First, after the foundation construction is completed, it is necessary to verify whether its bearing capacity meets the design requirements to avoid settlement problems after subsequent frame installation.
- Second, measure the foundation surface elevation to ensure the error is controlled within the allowable range of specifications.
- Third, check the embedded bolts — as the core components connecting steel members to the foundation, it is necessary to inspect whether their position, verticality, and exposed length meet the standards. Excessive position deviation will directly affect the installation accuracy of steel columns.
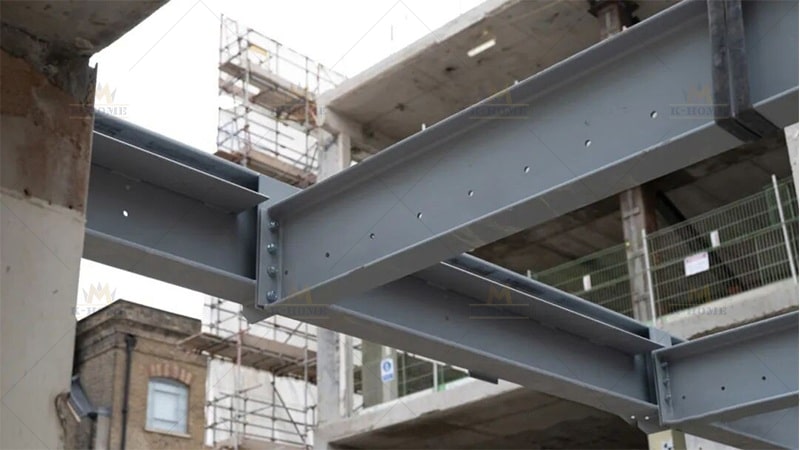
Step 3: Critical Part of Steel Frame Installation
Core installation (hoisting and connection) is a critical link in Steel Frame Structure Installation and must be operated in strict accordance with the sequence:
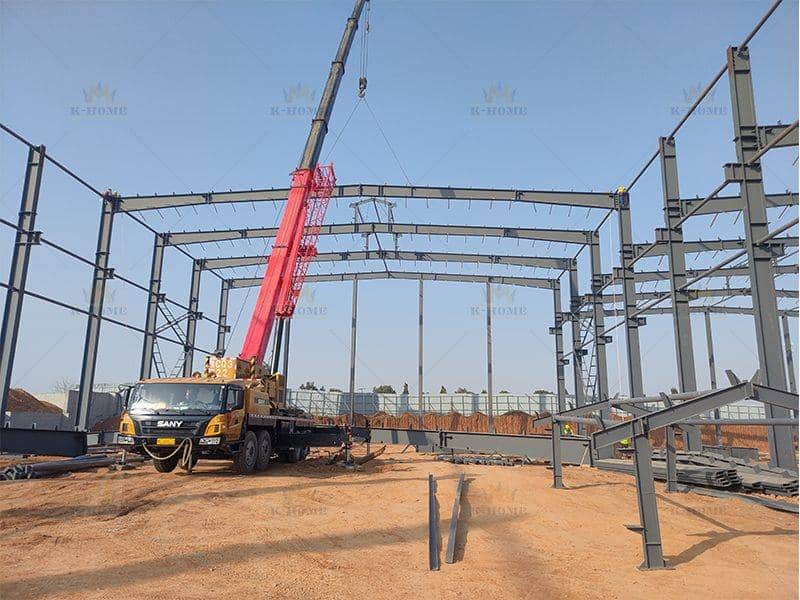
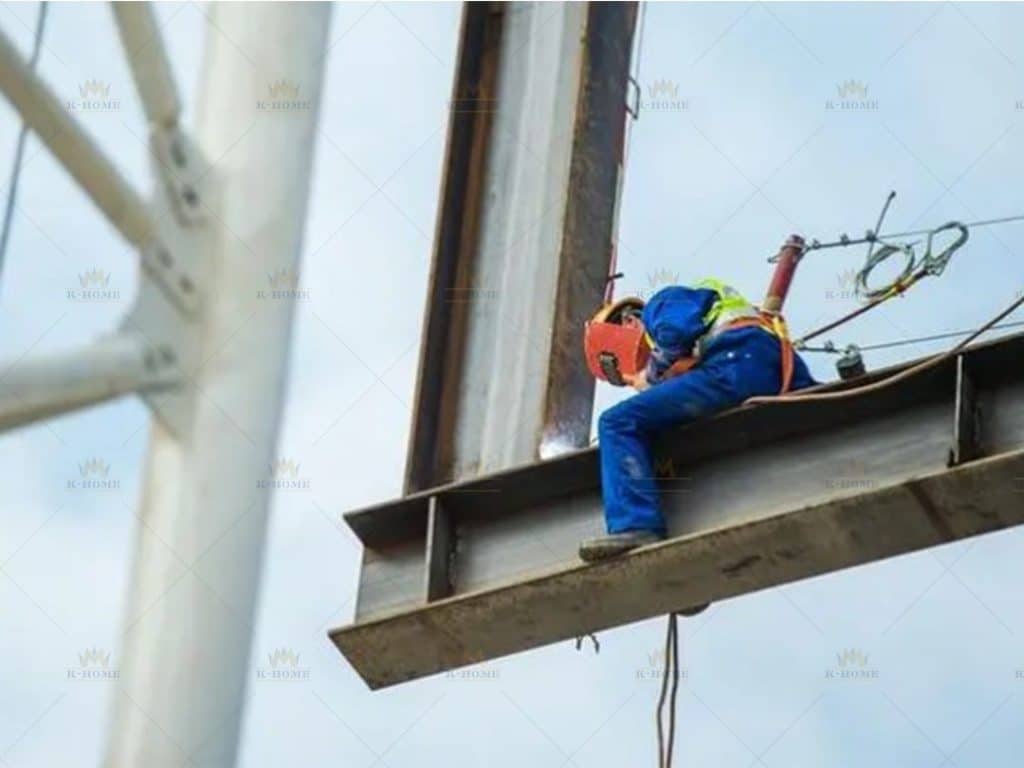
First, conduct hoisting preparation: select suitable hoisting equipment (such as truck cranes, tower cranes) according to the weight and size of steel components. When determining the hoisting points, avoid the weak parts of the components to prevent tilting during hoisting. At the same time, inspect the wear of hoisting tools, such as steel wire ropes and hooks, to ensure operational safety. Then carry out hoisting in the sequence of “install steel columns first, then steel beams, from bottom to top”: first hoist the steel columns to the designated position, connect them with the embedded foundation bolts and fix them temporarily, then hoist the steel beams and align them with the steel column connection nodes.
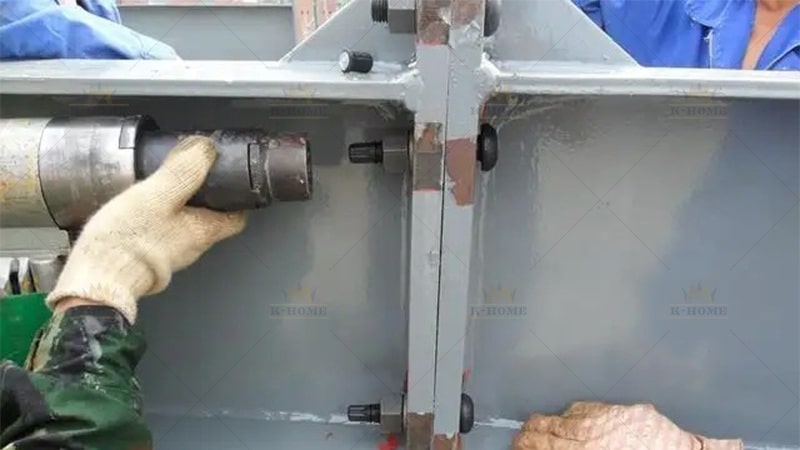
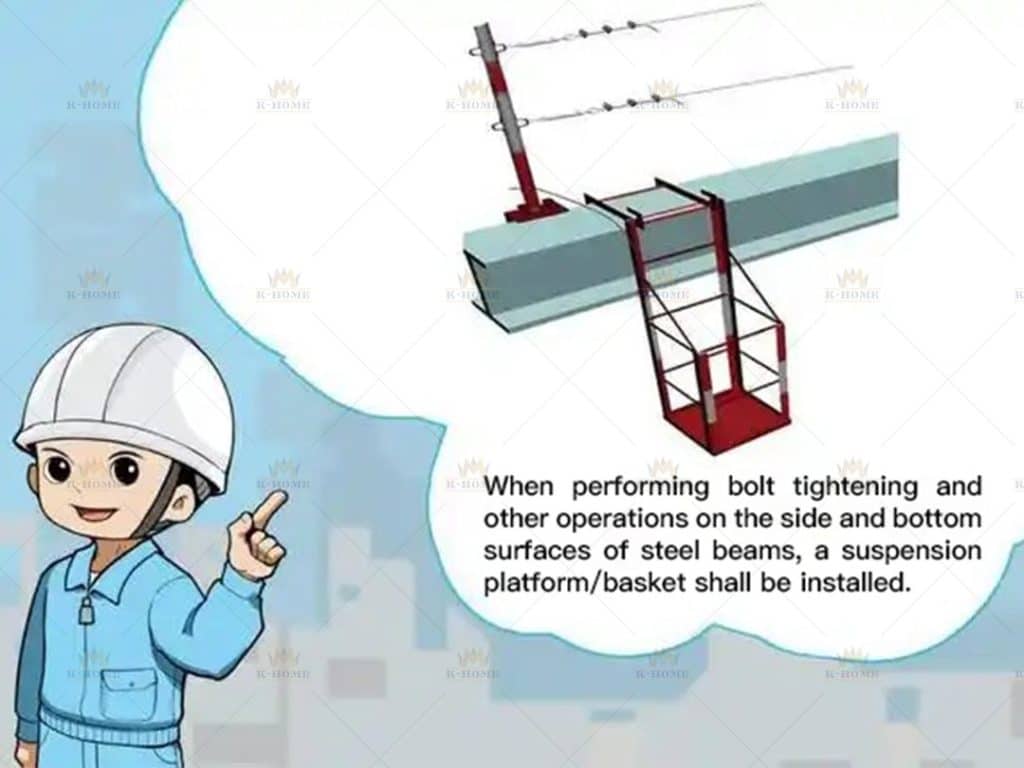
Finally, complete the fixation. Two common methods are used: high-strength bolts need to be tightened to the specified torque to avoid loosening; during welding, the current and voltage should be well controlled to ensure the weld height and length meet the design requirements and prevent problems such as incomplete penetration and cracks.
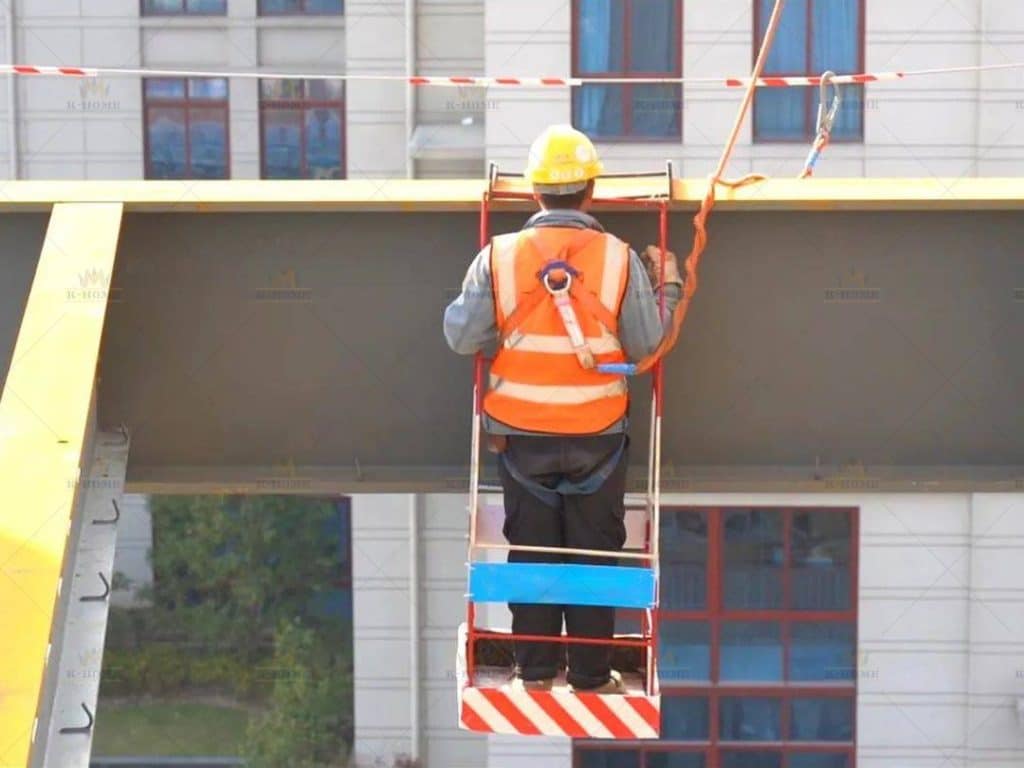
Step 4: Steel Frame Alignment for Correcting Frame Deviations
After hoisting is completed, you cannot directly enter the subsequent process, and you need to correct the frame deviation first. During a specific operation, use a level to detect the levelness of steel beams, and use a total station to measure the verticality of steel columns and the overall axis deviation of the frame.
- If the steel column verticality deviation exceeds standards, adjust the nuts of embedded foundation bolts or add appropriate iron sheets at the bottom of the steel columns for fine adjustment.
- If the steel beam levelness is unsatisfactory, adjust the thickness of the gaskets at the connection nodes between steel beams and columns.
Conduct correction in stages and re-inspect after each adjustment until all indicators meet specifications — for example, the verticality deviation of steel columns shall not exceed 1/1000 of the column height.
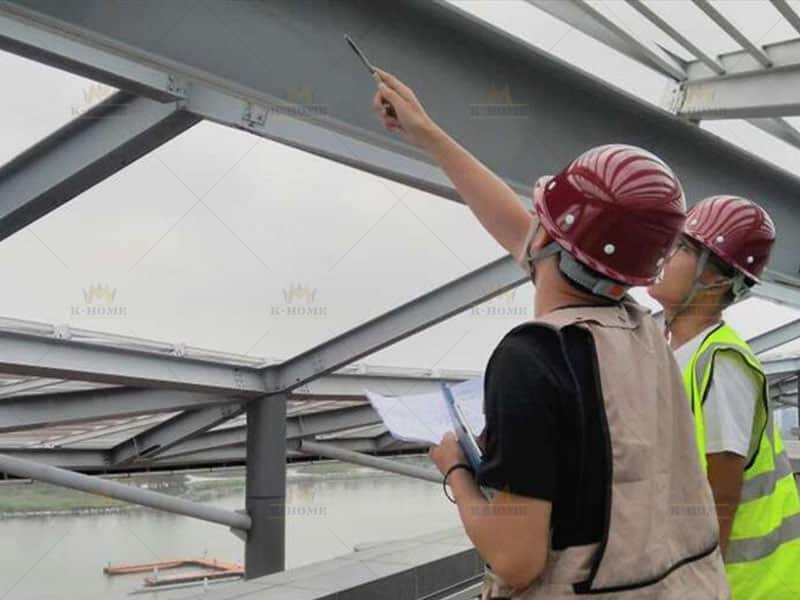
Step 5 for Steel Structure Installation: Finalize Installation Acceptance
Acceptance is the final critical link of Steel Frame Structure Installation and must be conducted in accordance with design drawings and industry standards. Focus on verifying:
Acceptance is the final critical phase of steel frame installation, conducted in line with design drawings and industry norms. Focus on verifying the compliance of steel components’ axes and elevations, checking if bolt tightening torque meets standards, confirming welded joint quality via visual inspection or non-destructive testing (NDT), and ensuring the frame’s verticality and levelness deviations stay within specified allowable ranges.
Crucial Considerations for Steel Frame Structure Installation: Effectively Mitigate Safety Risks
Safety Protocols for Steel Frame Installers in Steel Frame Structure Installation
The safety of steel frame installers is a prerequisite for steel frame construction, requiring strict adherence to installation safety requirements. All personnel must wear hard hats when entering the construction site; when working at height, they must fasten safety belts and wear non-slip shoes to prevent falls.
For high-altitude tasks, throwing tools or components is forbidden—tools should be securely stored in tool bags. For hoisting operations, warning zones must be marked under crane booms, with dedicated staff directing to keep people out of danger zones. Additionally, regularly check the performance of hoisting and welding equipment. If abnormal noises or faults are detected, halt use immediately; equipment can only return to operation after passing repairs, ensuring safety at all stages.
Material Quality Control for Steel Frame Structure Installation
Material quality control for steel structures centers on two vital aspects: The steel used must meet the strength grade specified in the design and come with complete material certification—severely rusted, cracked, or unmarked steel must not be used. Auxiliary materials like high-strength bolts, welding supplies, and gaskets must precisely match the steel model and have valid quality certificates. For instance, high-strength bolts require torque coefficient test reports to prevent connection failure of steel components due to substandard auxiliaries.
Adapting to Environmental Factors in Steel Frame Construction
Environmental conditions can affect the progress and quality of Steel Frame Structure Installation, requiring proactive responses:
- For rainy weather: Avoid open-air welding (rain impairs weld quality) by setting up temporary rain shelters. Cover installed steel components with waterproof cloth to prevent rust.
- In high winds: Halt high-altitude hoisting when wind speeds exceed Level 6—strong winds cause component sway, making positioning difficult and potentially triggering safety incidents.
- In high temperatures: Monitor thermal deformation of steel during welding, adjusting sequences (e.g., segmental welding) as needed. Provide cooling measures for installers to prevent heatstroke.
Contact Us >>
Have questions or need help? Before we start, you should know that almost all prefab steel buildings are customized.
Our engineering team will design it according to local wind speed, rain load, length*width*height, and other additional options. Or, we could follow your drawings. Please tell me your requirement, and we will do the rest!
Use the form to reach out and we will be in touch with you as quickly as possible.
About Author: K-HOME
K-home Steel Structure Co., Ltd covers an area of 120,000 square meters. We are engaged in the design, project budget, fabrication, and installation of PEB steel structures and sandwich panels with second-grade general contracting qualifications. Our products cover light steel structures, PEB buildings, low-cost prefab houses, container houses, C/Z steel, various models of color steel plate, PU sandwich panels, eps sandwich panels, rock wool sandwich panels, cold room panels, purification plates, and other construction materials.