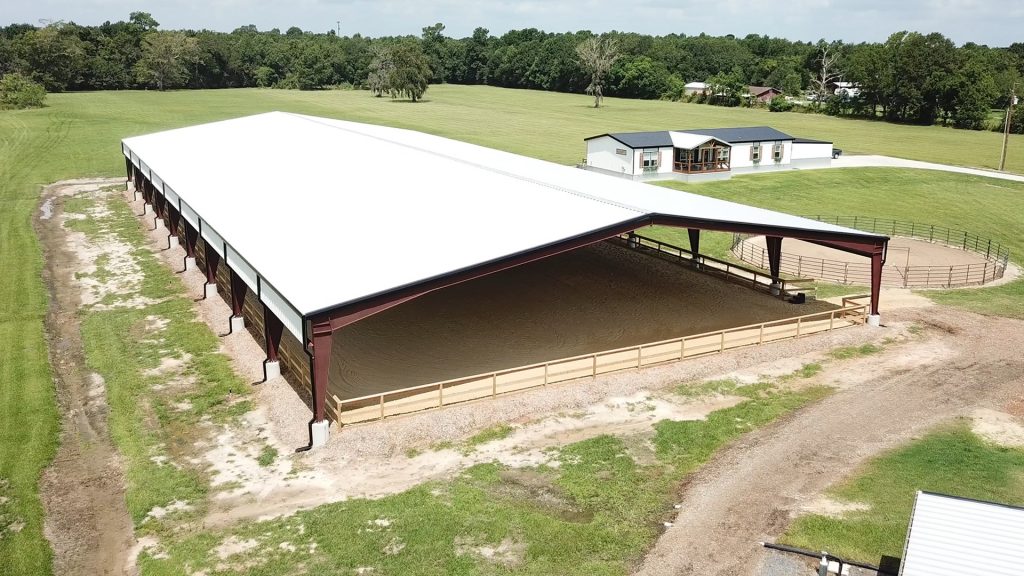
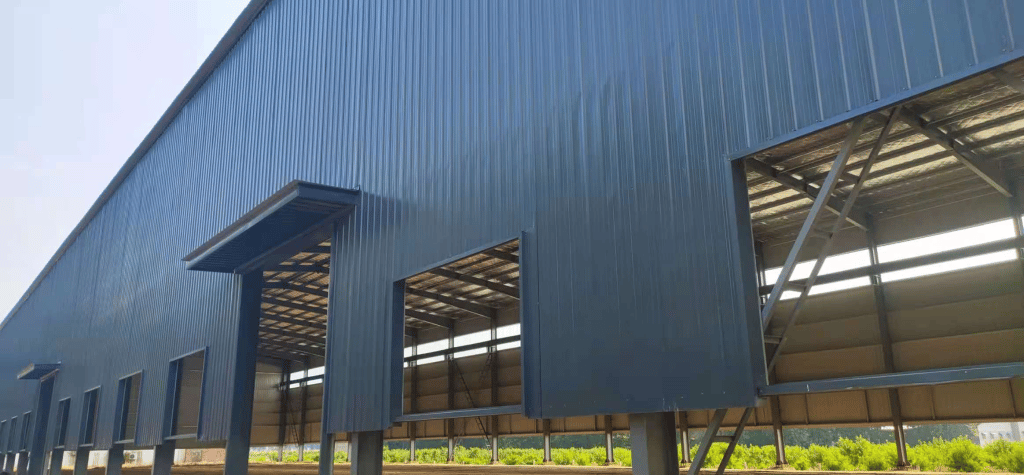
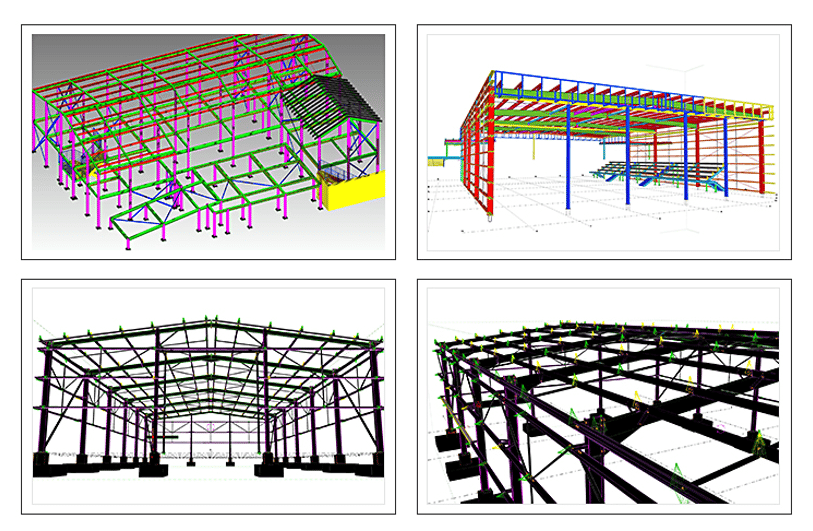
What is a Bracing System in the Steel Structure?
Steel structure buildings are widely used in various industries as warehouses and workshops, because they offer excellent structural strength, seismic resistance, and fire resistance.
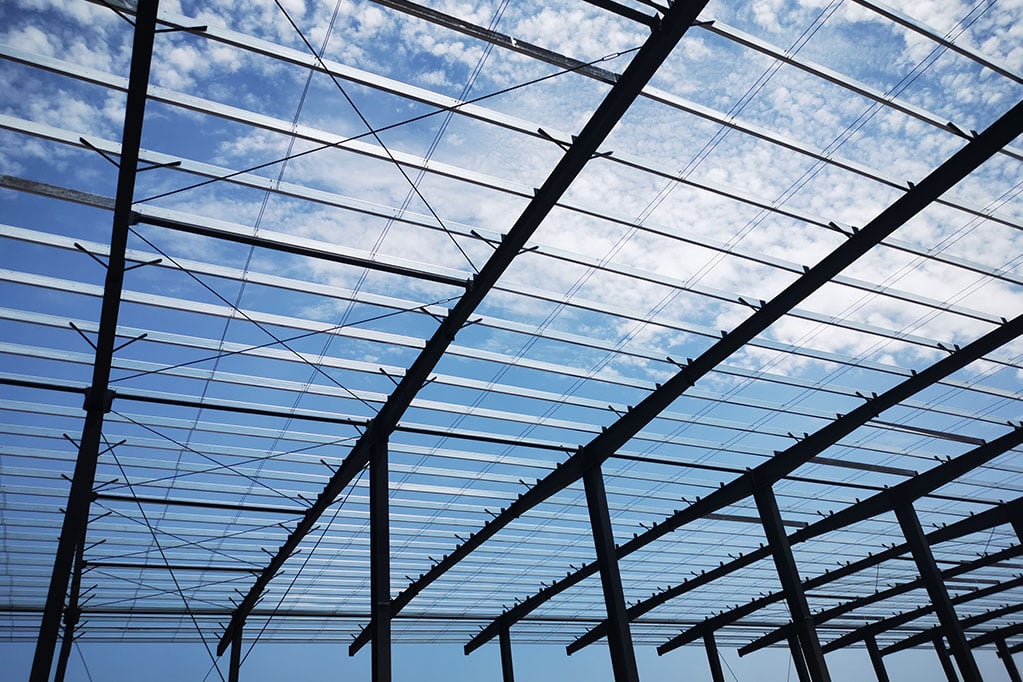
The bracing system is a member of the secondary structural in a steel structure, but it is also an indispensable part.
In portal frame steel structures, the bracing system plays a crucial role. This is mainly reflected in:
- For structures with complex floor plans, the bracing system also facilitates the adjustment of structural stiffness, making the structure more uniform and rationally stressed, and improving its overall integrity.
- Ensuring the stability of the overall structure and individual components.
- Transferring horizontal forces to the foundation and auxiliary installation works, etc.
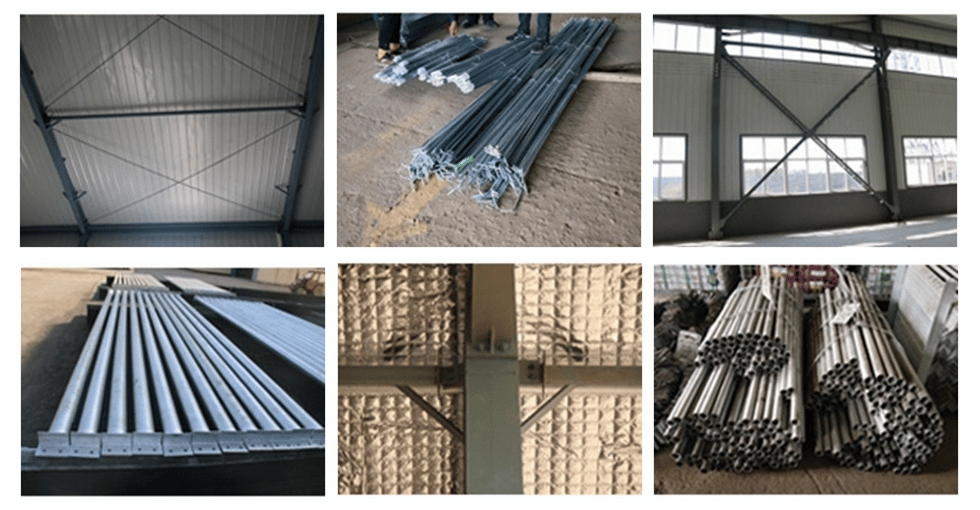

Further Reading: Steel Building Plans and Specifications
Different Types of Bracing Systems in Steel Structures
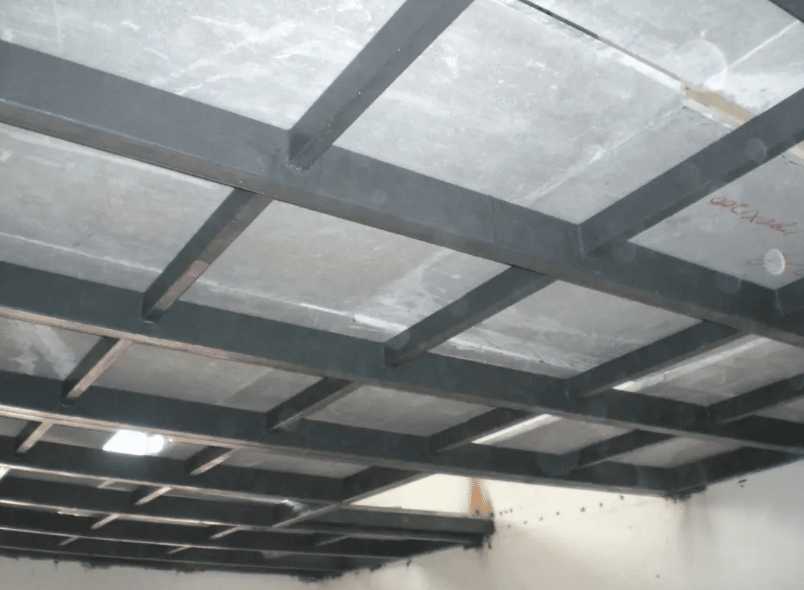
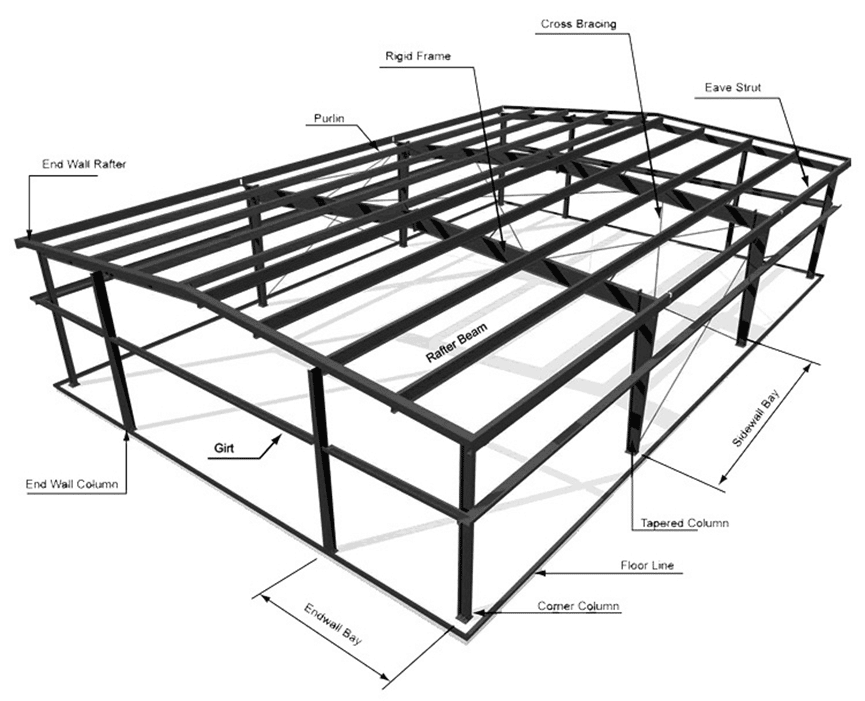
The bracing system is composed of various support components (such as structural steel, steel pipes, and reinforced concrete components) assembled by bolts, welding, or snap-fit connections. It can be divided into: roof bracing system, column bracing system, and other auxiliary bracing systems.
Roof Bracing System
The roof structure consists of purlins, roof trusses or roof beams, brackets or joists, and skylight frames. It bears the roof load and is connected as a whole by roof supports.
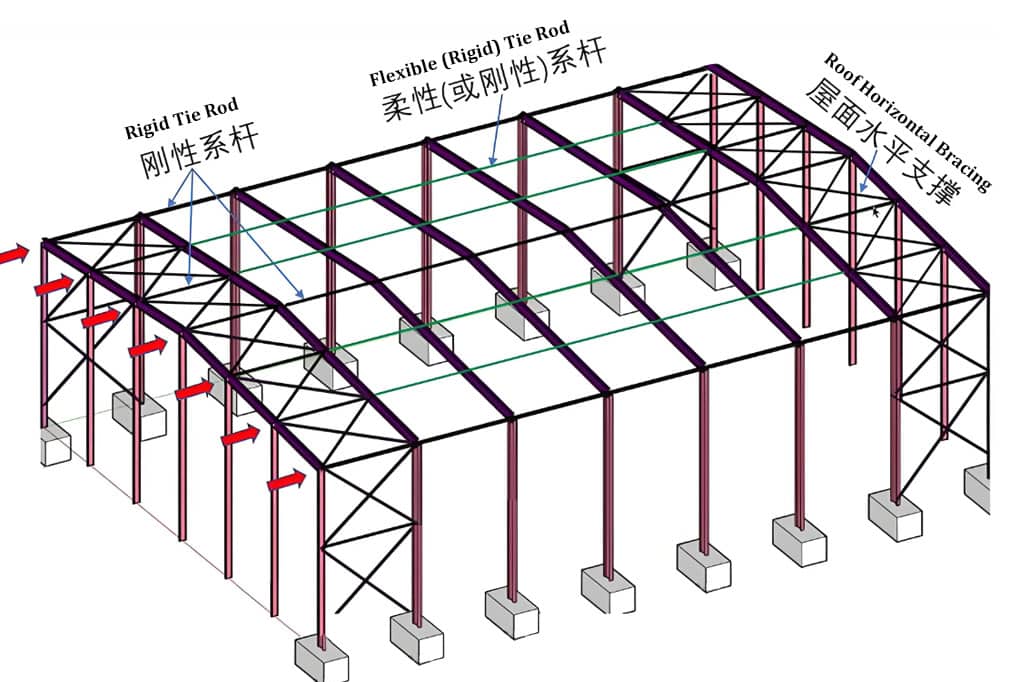
The roof support system includes lateral supports, longitudinal supports, vertical supports, tie rods, and corner braces. Its function is to improve the overall stiffness of the roof structure, fully utilize the structure’s spatial function, ensure the geometric stability of the structure, the lateral stability of the compression members, and the safety during structural installation.
The roof supports and inter-column supports together constitute the factory building’s support system. Their function is to connect the individual planar structural systems into a spatial whole. Within an independent temperature zone, it ensures the necessary stiffness and stability of the factory building structure while bearing both vertical and horizontal loads.
Column Bracing System
Inter-column bracing is an important component in steel structure systems used to enhance structural stability and transfer horizontal loads (such as wind loads and seismic forces).
It is typically placed between adjacent steel columns. Its function is to improve the lateral stiffness and overall integrity of the structure, reduce the calculated length of the columns, and prevent lateral instability or deformation of the columns under stress.
The main functions of inter-column bracing are:
- Lateral force resistance: Resisting horizontal loads (wind loads, seismic forces) and reducing structural lateral displacement.
- Stability assurance: Restricting lateral displacement of columns, reducing the slenderness ratio of the columns, and improving compressive stability.
- Load transfer: Transferring horizontal loads to the foundation or other lateral force-resisting members (such as shear walls).
- Construction-stage stability: Providing temporary stability during the installation of the steel structure.
Based on their orientation, inter-column bracing can be classified into two types: transverse bracing and longitudinal bracing.
- Transverse bracing: Perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the building, resisting lateral horizontal forces (such as wind loads).
- Longitudinal bracing: Arranged along the longitudinal axis of the building, resisting longitudinal horizontal forces.
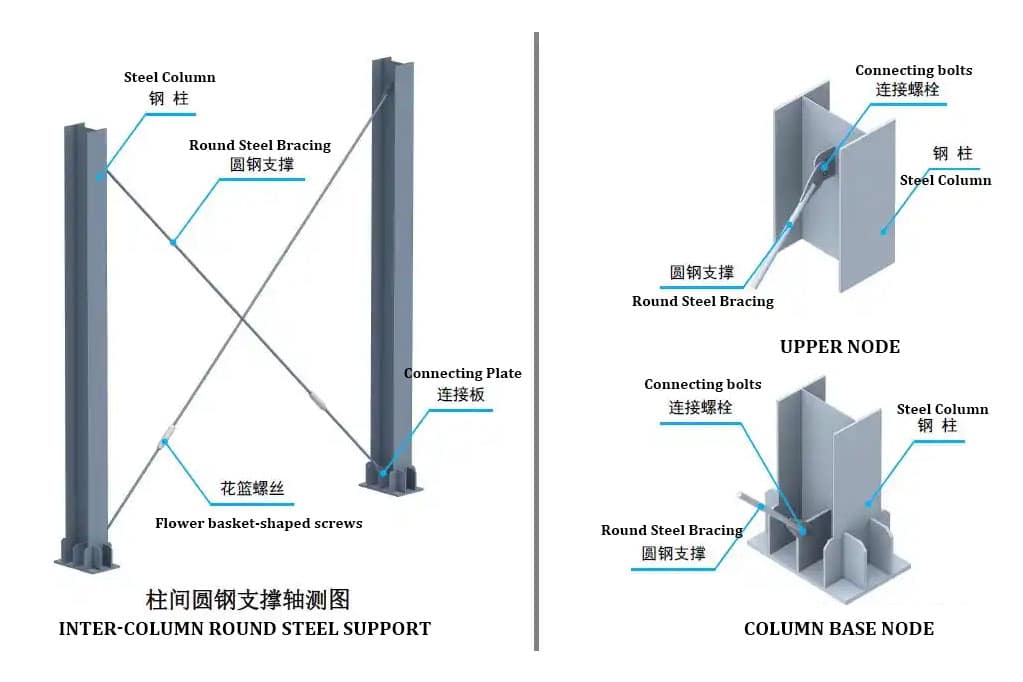
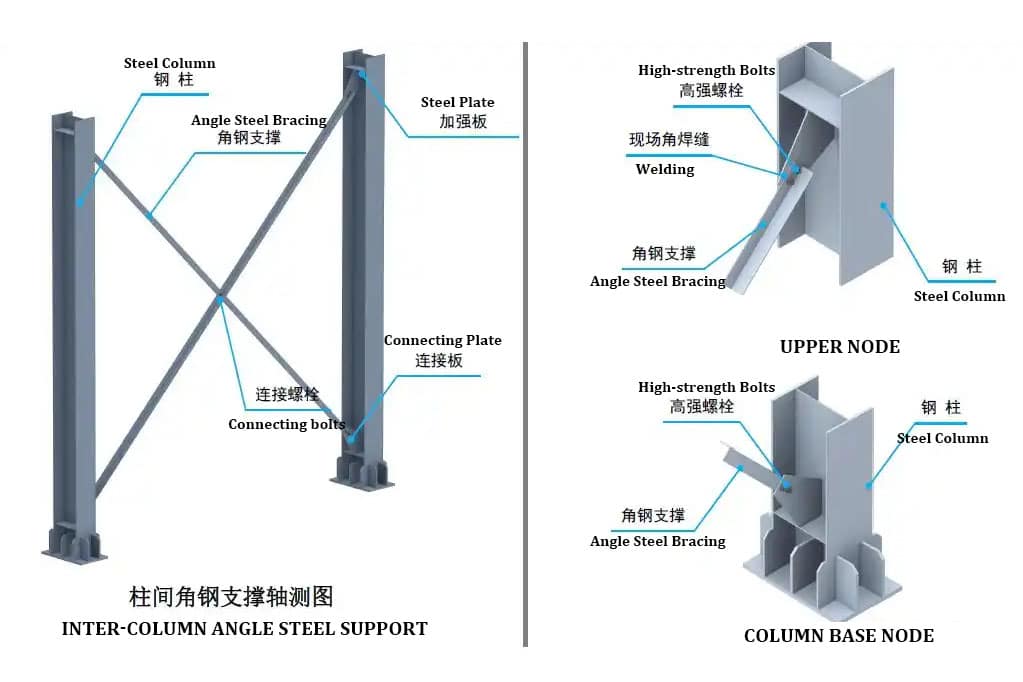
Longitudinal supports are divided into round steel supports, angle steel supports.
column bracing system – Longitudinal round steel bracing column bracing system – Longitudinal angle steel bracing
In practical applications, the appropriate form of column bracing needs to be selected based on the specific building structure and requirements. Furthermore, relevant codes and standards must be followed during the design and construction process to ensure the safety and stability of the column bracing.
It is better to use one type of inter-column bracing in the same building, and it is not advisable to mix several types of inter-column bracing. If due to functional requirements such as opening doors, windows or other factors, rigid frame support or truss support can be used. When the support system must be used in combination, the rigidity should be as consistent as possible. If the rigidity cannot be met, the longitudinal horizontal force borne by each support should be analyzed in detail to ensure the stability and safety of the structural symmetry.
Angle Brace
Angle braces are unique to solid-web portal rigid frame light steel structure buildings. The angle brace is arranged between the lower flange of the rigid frame inclined beam and the purlin or between the inner flange of the rigid frame side column and the wall beam. It supports the stability of rigid frame inclined beams and rigid frame side columns. The angle brace is an auxiliary member that does not become a system independently.
The function of the rigid frame inclined beam angle brace is to prevent the lateral instability of the inclined beam when the lower wing is compressed.
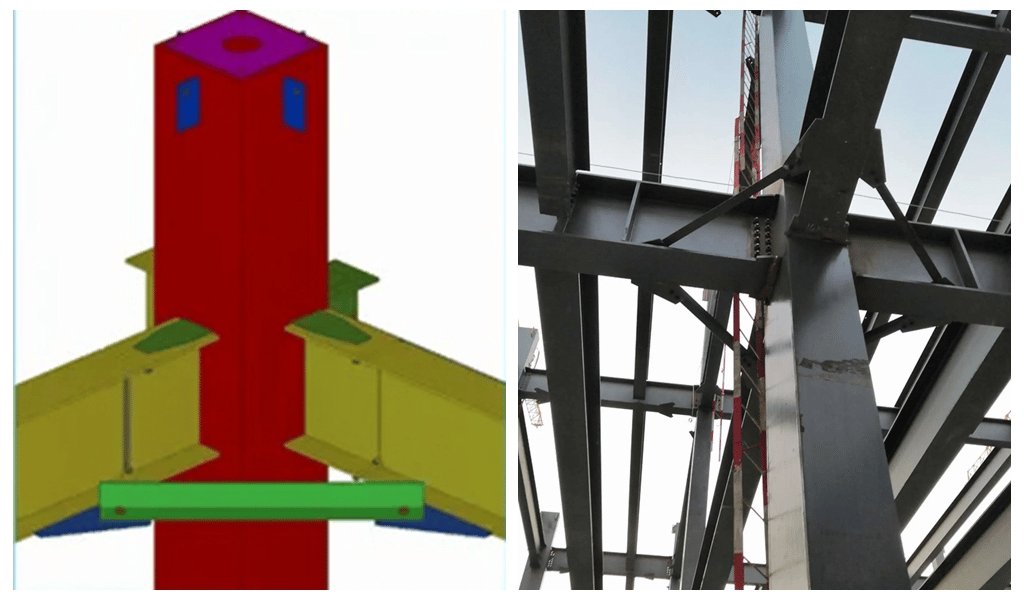
Angle iron is generally used for corner bracing, and the angle between the corner bracing and purlin or wall beam should not be less than 35°, and the minimum angle steel L40*4 can be used. Corner braces are bolted to beams or side columns and purlins or wall beams.
In general, the angle brace should be installed in the full span of the rigid frame inclined beam, mainly considering the possibility of the flange of the beam being compressed under the action of wind load, it can be installed only in the area where the lower flange of the beam is compressed near the support.
Bracing System Setting Principles
- Clearly, reasonably and simply transmit the longitudinal load, and shorten the force transmission path as much as possible;
- Ensure the out-of-plane stability of the structural system, and provide lateral support points for the overall stability of the structure and components;
- It is convenient to install the structure;
- Meet the necessary strength and stiffness requirements and have reliable connections.
Further Reading: Steel Structure Installation & Design
The PEB Steel Building
The Other Additional Attachments
Building FAQs
- How to Design Steel Building Components & Parts
- How Much Does a Steel Building Cost
- Pre-Construction Services
- What is a Steel Portal Framed Construction
- How to Read Structural Steel Drawings
Blogs Selected for You
- The Main Factors Affecting The Cost of Steel Structure Warehouse
- How Steel Buildings Help Reduce Environmental Impact
- How to Read Structural Steel Drawings
- Are Metal Buildings Cheaper Than Wood Buildings?
- Benefits of Metal Buildings For Agricultural Use
- Choosing the Right Location For Your Metal Building
- Making a Prefab Steel Church
- Passive Housing & Metal –Made for Each Other
- Uses for Metal Structures You May Not Have Known
- Why Do You Need a Prefabricated Home
- What Do You Need To Know Before Designing a Steel Structure Workshop?
- Why Should You Choose a Steel Frame Home Over a Wooden Frame Home
Contact Us >>
Have questions or need help? Before we start, you should know that almost all prefab steel buildings are customized.
Our engineering team will design it according to local wind speed, rain load, length*width*height, and other additional options. Or, we could follow your drawings. Please tell me your requirement, and we will do the rest!
Use the form to reach out and we will be in touch with you as quickly as possible.
About Author: K-HOME
K-home Steel Structure Co., Ltd covers an area of 120,000 square meters. We are engaged in the design, project budget, fabrication, and installation of PEB steel structures and sandwich panels with second-grade general contracting qualifications. Our products cover light steel structures, PEB buildings, low-cost prefab houses, container houses, C/Z steel, various models of color steel plate, PU sandwich panels, eps sandwich panels, rock wool sandwich panels, cold room panels, purification plates, and other construction materials.